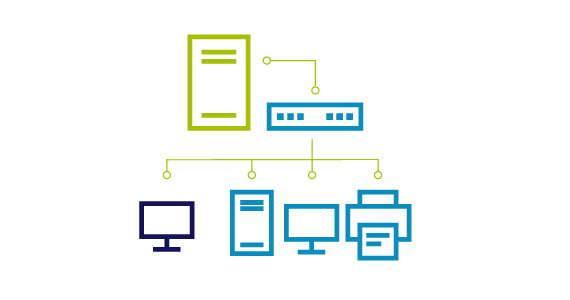
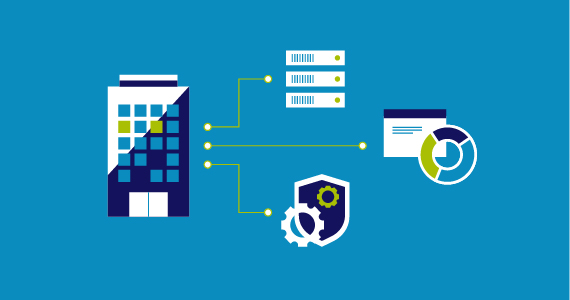
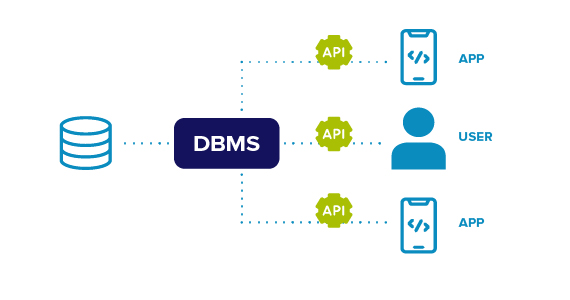
IT Management and Security Learning Hub
IT Management and Security Learning Hub
Welcome to the IT Management and Security Learning Hub where we cover comprehensive cybersecurity, data and infrastructure management topics to help you better understand, manage and secure your data, applications and critical infrastructure whether on-premises or in the cloud.